RNase P RNA
- RNA sequences : see data set
- Results of Carnac (CT files) : structure 1, structure 2, structure 3, structure 4, structure 5
We have selected the Delta/Epsilon Purple Bacteria RNase P sequences available in the RNaseP database developped by J.W. Brown. These RNAs present a common structure, in spite of the weak sequence conservation (60% of identity in average). We kept only full and non redundant sequences. This gives five sequences: D.desulfuricans (M59357), D.vulgaris, G.sulfurreducens, C.jejuni (AL139075), H.pylori (AE000573). We compare the secondary structure predicted by Carnac to the reference structure provided by the database. For the reference organism (D.desulfuricans), the real structure has around 15 stems, plus 2 pseudoknots. Some stems are not present in the structure of the other organisms.
| Organism | Number of predicted stems | Correctness percentage |
|---|---|---|
| D.desulfuricans | 11 | 100% |
| D.vulgaris | 10 | 100% |
| G.sulfurreducens | 10 | 100% |
| C.jejuni | 11 | 81% |
| H.pylori | 11 | 81% |
Usual thermodynamic folding programs that work with a single sequence usually fail on that data set.
Ciliate telomerase RNA
- RNA sequences : see data set
- Results of Carnac (CT files) : structure 1, structure 2, structure 3
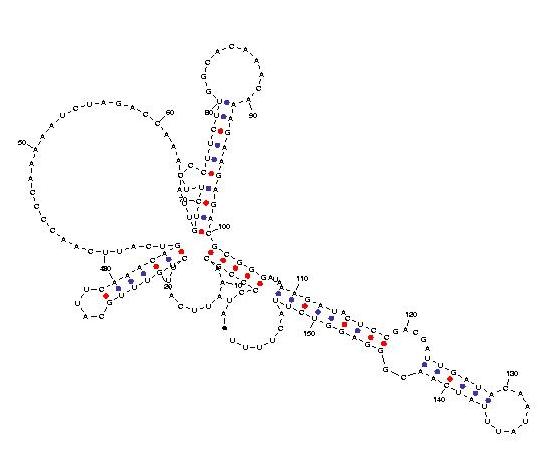
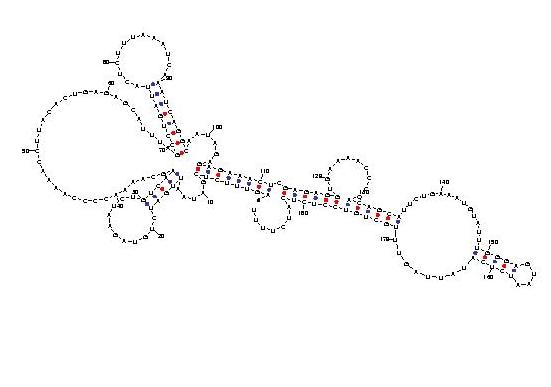
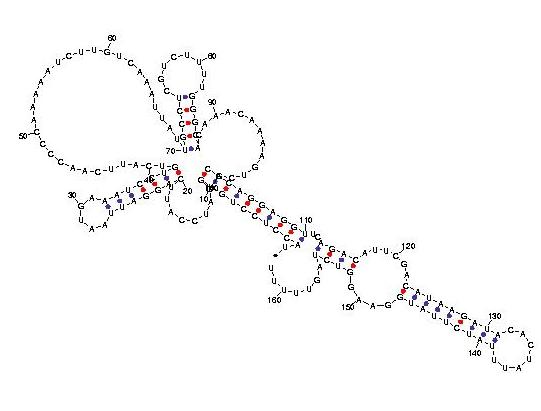
Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein reverse transcriptase that synthesises telomeric DNA. Sequences are available from the RFAM database, with accession number RF00025. We selected three sequences with poor primary structure conservation, that can not be correctly aligned with usual multiple alignment automatic methods. The three structures predicted by Carnac are consistent with the model available in RFAM.
When there is no structure : Enterovirus
- RNA sequences : see data set
- Results of Carnac (CT files) : structure 1, structure 2, structure 3, structure 4, structure 5, structure 6, structure 7, structure 8, structure 9, structure 10, structure 11
The program may also be used to analyze RNA sequences that are not functionnaly structured, or only with a partial structure. We ran Carnac on a set of messenger RNA sequences of enterovirus, coding for a polyprotein: each sequence is 1800 nt long, and is composed of 5'UTR (700 nt approximately) and the beginning of the ORF (1100 nt approximately) . The 5' UTR is believed to share a common structure, but not the coding region (Le SY, Zuker M.). The figure below shows that all stems predicted by Carnac are located in the 5'UTR, before the START codon.'











